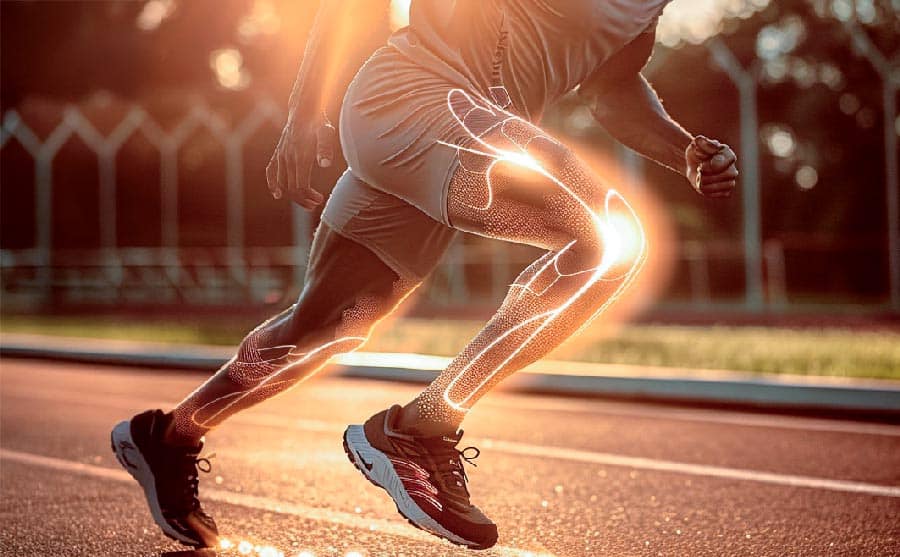
U-MSC and Derived Exosomes for Sports Injuries
Stem Cell Therapies for Athletes' Healing and Recovery
Embrace the latest non-invasive therapeutic options with minimal downtime, designed to support athletes in their recovery.
Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell (U-MSC) and Exosomes Therapies for Sports Injuries
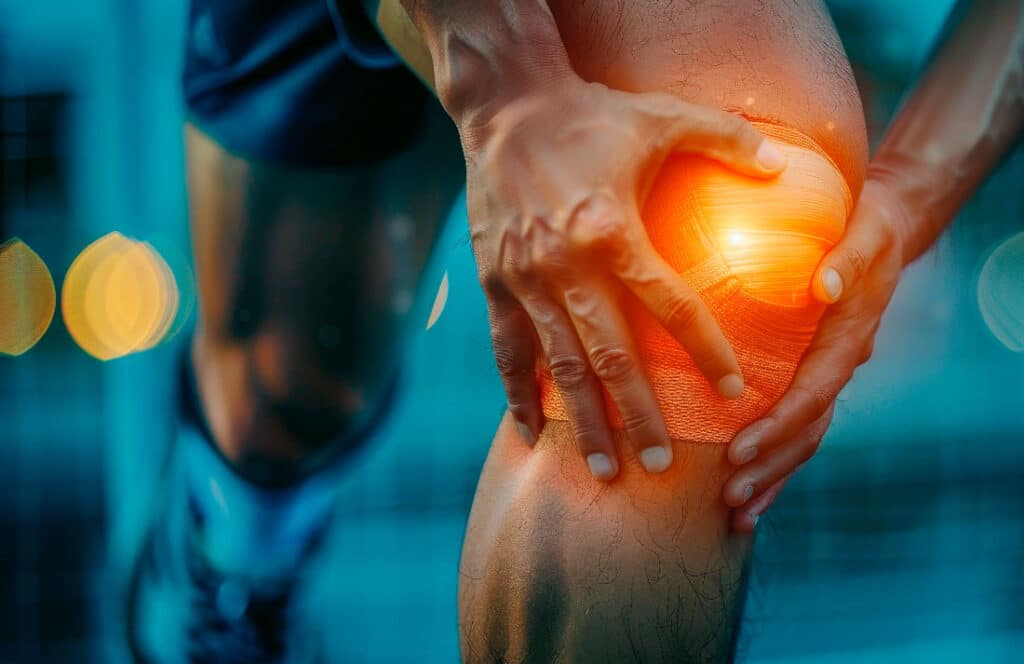
Sports injuries can range from acute strains to chronic joint and tissue damage. These setbacks not only hinder performance but impact overall well-being. Traditional treatments often focus on symptom relief, but at OmniStem, we target healing at the cellular level, leveraging the natural power of U-MSC and exosome-based therapies.
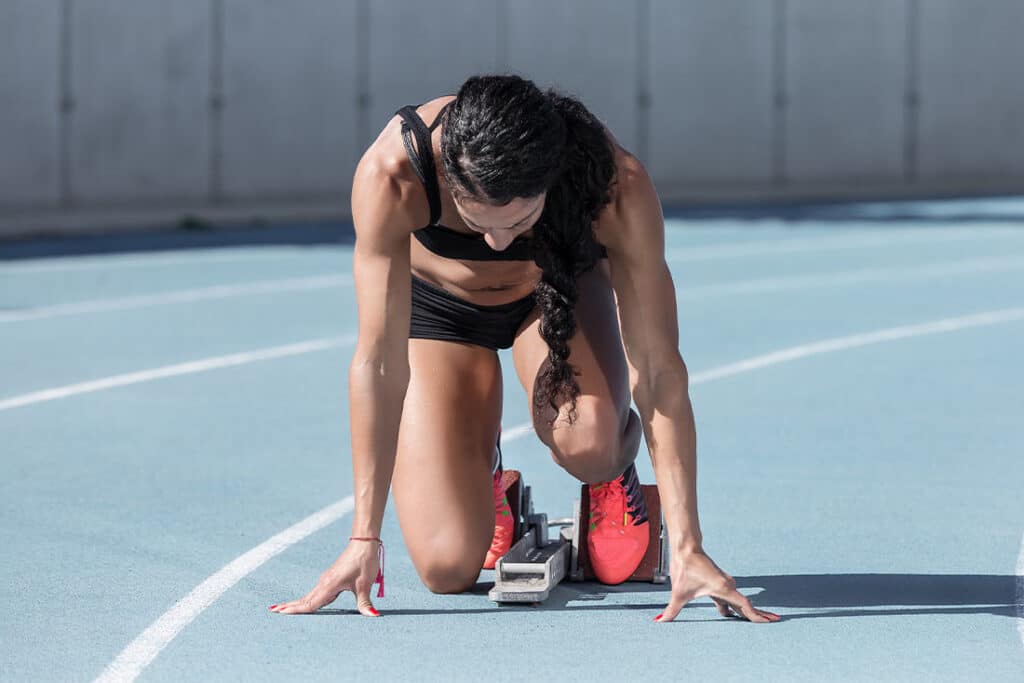

Targeted Healing
U-MSC therapies promote precise healing and regeneration. This targeted approach is essential for profesional athletes, who often suffer location specific injuries that require focused treatment.

Reduce Inflammation
By harnessing the anti-inflammatory properties of U-MSC, athletes can experience a significant reduction in post-injury swelling and pain, leading to quicker rehabilitation starts.

Enhanced Performance
Beyond healing, U-MSC therapies aim to restore and potentially enhance the athletic capabilities of sports professionals, aiding in achieving peak performance post-recovery.
An Alternative Approach to Treating Sports Injuries
OmniStem provides professional athletes with cutting-edge, alternative treatments designed to enhance recovery and performance. Our U-MSC therapies offer non-invasive solutions to help athletes achieve their full potential.
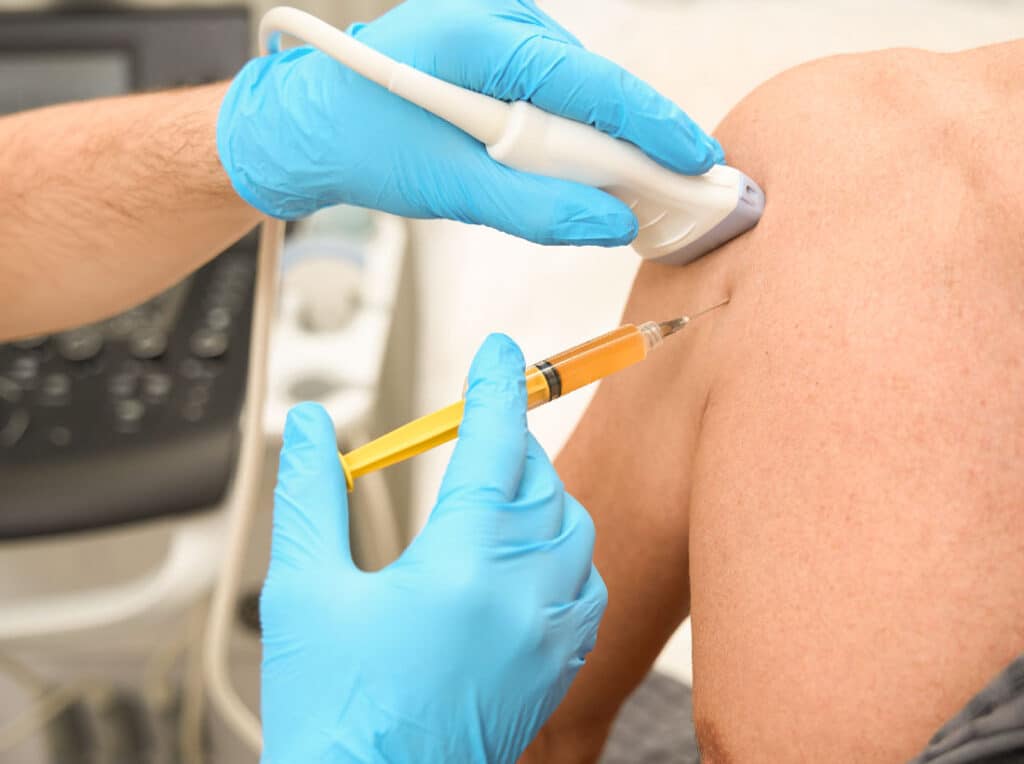
Key Benefits of U-MSC Therapy for Athletes
Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells combined with U-MSC derived exosomes, delivers a multi-dimensional approach to recovery.
Anti-Inflammatory Support
Inflammation is a natural response to injury but can sometimes hinder recovery. U-MSC therapies help regulate inflammation, creating a supportive environment for the body’s natural healing processes.
Tissue Regeneration
U-MSCs are highly versatile and can differentiate into the cells needed to repair torn muscles, ligaments, or tendons. By integrating into the injured area, they support tissue regeneration restoring functionality.
Trophic Support
Immunomodulation
U-MSCs and exosomes help regulate immune activity, guiding immune cells to protect the tissue and support balanced healing.
OmniStem’s regenerative medicine approach optimizes the body’s intrinsic repair mechanisms without introducing foreign agents. This natural healing strategy not only restores athletes to their pre-injury state but can also improve joint functionality and muscle strength, enhancing overall performance and reducing the risk of reinjury.

U-MSC
U-MSC Derived Exosomes
Advancing Biologics in Regenerative Medicine
U-MSC are a valuable biologic option in regenerative medicine due to their ability to support the repair, replacement, and rejuvenation of damaged or malfunctioning cells. They hold promise for addressing a variety of medical conditions, including autoimmune diseases, neurological complications, chronic pain, and sports injuries.

Wang, Hao-Nan; Rong, Xiao; Yang, Lu-Ming; Hua, Wei-Zhong; Nicorresponding, Guo-Xin
Advances in Stem Cell Therapies for Rotator Cuff Injuries Journal Article
In: 2022.
@article{nokey,
title = {Advances in Stem Cell Therapies for Rotator Cuff Injuries},
author = {Hao-Nan Wang and Xiao Rong and Lu-Ming Yang and Wei-Zhong Hua and Guo-Xin Nicorresponding},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9174670/},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-05-25},
abstract = {Rotator cuff injury is a common upper extremity musculoskeletal disease that may lead to persistent pain and functional impairment. Despite the clinical outcomes of the surgical procedures being satisfactory, the repair of the rotator cuff remains problematic, such as through failure of healing, adhesion formation, and fatty infiltration. Stem cells have high proliferation, strong paracrine action, and multiple differentiation potential, which promote tendon remodeling and fibrocartilage formation and increase biomechanical strength. Additionally, stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) can increase collagen synthesis and inhibit inflammation and adhesion formation by carrying regulatory proteins and microRNAs. Therefore, stem cell-based therapy is a promising therapeutic strategy that has great potential for rotator cuff healing. In this review, we summarize the advances of stem cells and stem cell-derived EVs in rotator cuff repair and highlight the underlying mechanism of stem cells and stem cell-derived EVs and biomaterial delivery systems. Future studies need to explore stem cell therapy in combination with cellular factors, gene therapy, and novel biomaterial delivery systems.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Ding, Guocheng; Du, Jianing; Hu, Xiaoqing; Yingfang,
Mesenchymal Stem Cells From Different Sources in Meniscus Repair and Regeneration Journal Article
In: 2022.
@article{nokey,
title = {Mesenchymal Stem Cells From Different Sources in Meniscus Repair and Regeneration},
author = {Guocheng Ding and Jianing Du and Xiaoqing Hu and Yingfang},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9091333/},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-04-27},
urldate = {2022-04-27},
abstract = {Meniscus damage is a common trauma that often arises from sports injuries or menisci tissue degeneration. Current treatment methods focus on the repair, replacement, and regeneration of the meniscus to restore its original function. The advance of tissue engineering provides a novel approach to restore the unique structure of the meniscus. Recently, mesenchymal stem cells found in tissues including bone marrow, peripheral blood, fat, and articular cavity synovium have shown specific advantages in meniscus repair. Although various studies explore the use of stem cells in repairing meniscal injuries from different sources and demonstrate their potential for chondrogenic differentiation, their meniscal cartilage-forming properties are yet to be systematically compared. Therefore, this review aims to summarize and compare different sources of mesenchymal stem cells for meniscal repair and regeneration.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Stewart, Claire E.
Stem cells and regenerative medicine in sport science Journal Article
In: 2021.
@article{nokey,
title = {Stem cells and regenerative medicine in sport science},
author = {Claire E. Stewart},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-08-27},
abstract = {The estimated cost of acute injuries in college-level sports in the USA is ∼1.5 billion dollars annually, without considering the cost of follow-up rehabilitation. In addition to this huge financial burden, sports injuries may be career-ending for some athletes without appropriate diagnosis and relevant interventions. With a growing number of females participating in contact-based and pivoting sports, middle-aged individuals returning to sports,s and natural injuries of aging all increasing, such costs and negative implications for quality of life will expand. For those injuries that cannot be predicted and prevented, there is a real need to optimize repair, recovery, and function post-injury in the sporting and clinical worlds. The 21st century has seen rapid growth in regenerative medicine for sporting injuries to progress recovery and facilitate return to sport. Such interventions harness knowledge relating to stem cells as a potential for injury repair. While the field is rapidly growing, consideration beyond the stem cells to the factors they secrete should be considered in developing practical, affordable treatments.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Xu, Yue; Zhang, Wan-Xia; Wang, Li-Na; Ming, Yue-Qing; Li, Yu-Lin; Ni, Guo-Xin
Stem cell therapies in tendon-bone healing Journal Article
In: 2021.
@article{nokey,
title = {Stem cell therapies in tendon-bone healing},
author = {Yue Xu and Wan-Xia Zhang and Li-Na Wang and Yue-Qing Ming and Yu-Lin Li and Guo-Xin Ni},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8316867/},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-07-26},
abstract = {Tendon-bone insertion injuries such as rotator cuff and anterior cruciate ligament injuries are currently highly common and severe. The key method of treating this kind of injury is the reconstruction operation. The success of this reconstructive process depends on the ability of the graft to incorporate into the bone. Recently, there has been substantial discussion about how to enhance the integration of tendon and bone through biological methods. Stem cells like bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), tendon stem/progenitor cells, synovium-derived MSCs, adipose-derived stem cells, or periosteum-derived periosteal stem cells can self-regenerate and potentially differentiate into different cell types, which have been widely used in tissue repair and regeneration. Thus, we concentrate in this review on the current circumstances of tendon-bone healing using stem cell therapy.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Ajibadea, David A.; Vance, Danica D.; Harea, Joshua M.; Lesniak, Lee D. Kaplanand Bryson P.
Emerging Applications of Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine to Sports Injuries Journal Article
In: 2014.
@article{nokey,
title = {Emerging Applications of Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine to Sports Injuries},
author = {David A. Ajibadea and Danica D. Vance and Joshua M. Harea and Lee D. Kaplanand Bryson P. Lesniak},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4555618/},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-02-02},
abstract = {Cell-based therapies and regenerative medicine offer safe and potentially efficacious treatment for sports-related musculoskeletal injuries. Basic science and preclinical studies that support the possibility of enhanced recovery from sports injuries using cell-based therapies are accumulating; however, more clinical evidence is necessary to define the indications and parameters for their use. Accordingly, exposing patients to cell-based therapies could confer an unacceptable risk profile with minimal or no benefit. Continued clinical testing with animal models and clinical trials is necessary to determine the relative risks and benefits as well as the indications and methodology of treatment.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Wang, Hao-Nan; Rong, Xiao; Yang, Lu-Ming; Hua, Wei-Zhong; Nicorresponding, Guo-Xin
Advances in Stem Cell Therapies for Rotator Cuff Injuries Journal Article
In: 2022.
@article{nokey,
title = {Advances in Stem Cell Therapies for Rotator Cuff Injuries},
author = {Hao-Nan Wang and Xiao Rong and Lu-Ming Yang and Wei-Zhong Hua and Guo-Xin Nicorresponding},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9174670/},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-05-25},
abstract = {Rotator cuff injury is a common upper extremity musculoskeletal disease that may lead to persistent pain and functional impairment. Despite the clinical outcomes of the surgical procedures being satisfactory, the repair of the rotator cuff remains problematic, such as through failure of healing, adhesion formation, and fatty infiltration. Stem cells have high proliferation, strong paracrine action, and multiple differentiation potential, which promote tendon remodeling and fibrocartilage formation and increase biomechanical strength. Additionally, stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) can increase collagen synthesis and inhibit inflammation and adhesion formation by carrying regulatory proteins and microRNAs. Therefore, stem cell-based therapy is a promising therapeutic strategy that has great potential for rotator cuff healing. In this review, we summarize the advances of stem cells and stem cell-derived EVs in rotator cuff repair and highlight the underlying mechanism of stem cells and stem cell-derived EVs and biomaterial delivery systems. Future studies need to explore stem cell therapy in combination with cellular factors, gene therapy, and novel biomaterial delivery systems.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Ding, Guocheng; Du, Jianing; Hu, Xiaoqing; Yingfang,
Mesenchymal Stem Cells From Different Sources in Meniscus Repair and Regeneration Journal Article
In: 2022.
@article{nokey,
title = {Mesenchymal Stem Cells From Different Sources in Meniscus Repair and Regeneration},
author = {Guocheng Ding and Jianing Du and Xiaoqing Hu and Yingfang},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9091333/},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-04-27},
urldate = {2022-04-27},
abstract = {Meniscus damage is a common trauma that often arises from sports injuries or menisci tissue degeneration. Current treatment methods focus on the repair, replacement, and regeneration of the meniscus to restore its original function. The advance of tissue engineering provides a novel approach to restore the unique structure of the meniscus. Recently, mesenchymal stem cells found in tissues including bone marrow, peripheral blood, fat, and articular cavity synovium have shown specific advantages in meniscus repair. Although various studies explore the use of stem cells in repairing meniscal injuries from different sources and demonstrate their potential for chondrogenic differentiation, their meniscal cartilage-forming properties are yet to be systematically compared. Therefore, this review aims to summarize and compare different sources of mesenchymal stem cells for meniscal repair and regeneration.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Stewart, Claire E.
Stem cells and regenerative medicine in sport science Journal Article
In: 2021.
@article{nokey,
title = {Stem cells and regenerative medicine in sport science},
author = {Claire E. Stewart},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-08-27},
abstract = {The estimated cost of acute injuries in college-level sports in the USA is ∼1.5 billion dollars annually, without considering the cost of follow-up rehabilitation. In addition to this huge financial burden, sports injuries may be career-ending for some athletes without appropriate diagnosis and relevant interventions. With a growing number of females participating in contact-based and pivoting sports, middle-aged individuals returning to sports,s and natural injuries of aging all increasing, such costs and negative implications for quality of life will expand. For those injuries that cannot be predicted and prevented, there is a real need to optimize repair, recovery, and function post-injury in the sporting and clinical worlds. The 21st century has seen rapid growth in regenerative medicine for sporting injuries to progress recovery and facilitate return to sport. Such interventions harness knowledge relating to stem cells as a potential for injury repair. While the field is rapidly growing, consideration beyond the stem cells to the factors they secrete should be considered in developing practical, affordable treatments.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Xu, Yue; Zhang, Wan-Xia; Wang, Li-Na; Ming, Yue-Qing; Li, Yu-Lin; Ni, Guo-Xin
Stem cell therapies in tendon-bone healing Journal Article
In: 2021.
@article{nokey,
title = {Stem cell therapies in tendon-bone healing},
author = {Yue Xu and Wan-Xia Zhang and Li-Na Wang and Yue-Qing Ming and Yu-Lin Li and Guo-Xin Ni},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8316867/},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-07-26},
abstract = {Tendon-bone insertion injuries such as rotator cuff and anterior cruciate ligament injuries are currently highly common and severe. The key method of treating this kind of injury is the reconstruction operation. The success of this reconstructive process depends on the ability of the graft to incorporate into the bone. Recently, there has been substantial discussion about how to enhance the integration of tendon and bone through biological methods. Stem cells like bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), tendon stem/progenitor cells, synovium-derived MSCs, adipose-derived stem cells, or periosteum-derived periosteal stem cells can self-regenerate and potentially differentiate into different cell types, which have been widely used in tissue repair and regeneration. Thus, we concentrate in this review on the current circumstances of tendon-bone healing using stem cell therapy.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Ajibadea, David A.; Vance, Danica D.; Harea, Joshua M.; Lesniak, Lee D. Kaplanand Bryson P.
Emerging Applications of Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine to Sports Injuries Journal Article
In: 2014.
@article{nokey,
title = {Emerging Applications of Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine to Sports Injuries},
author = {David A. Ajibadea and Danica D. Vance and Joshua M. Harea and Lee D. Kaplanand Bryson P. Lesniak},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4555618/},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-02-02},
abstract = {Cell-based therapies and regenerative medicine offer safe and potentially efficacious treatment for sports-related musculoskeletal injuries. Basic science and preclinical studies that support the possibility of enhanced recovery from sports injuries using cell-based therapies are accumulating; however, more clinical evidence is necessary to define the indications and parameters for their use. Accordingly, exposing patients to cell-based therapies could confer an unacceptable risk profile with minimal or no benefit. Continued clinical testing with animal models and clinical trials is necessary to determine the relative risks and benefits as well as the indications and methodology of treatment.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Complete the form to receive detailed information about regenerative medicine therapies for sports injuries
- Secure HIPAA Compliant
- 48 Hours Response
- No Obligations
Prescreening Questionnaire
Start by filling out our Pre Screening Questionnaire and a member of our team will reach out to discuss your interest and answer any initial questions.
PATIENT INTAKE QUESTIONNAIRE
Please fill out the patient intake questionnaire. This information will help our team better understand your medical history and needs.
SCHEDULE A VIDEO CONSULTATION
Book a video consultation with our medical team. During this consultation, you may be asked to provide any relevant medical records or images for review.
Final Review
Our team will conduct a final review of your case, and we will outline the recommended next steps based on your consultation and submitted information.

OmniStem Cell-based Therapies
Frequently Asked Questions
Please explore our Resource Center for helpful information. If you have any additional questions, feel free to contact our patient care team for assistance.
Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (U-MSCs) are a type of adult stem cell found in Wharton’s jelly, a gelatinous substance within the umbilical cord. These cells have the ability to differentiate into various cell types, such as bone, cartilage, and fat cells, making them highly valuable for regenerative medicine and cell therapies.
Exosomes are microscopic, sac-like vesicles naturally released by cells, containing a rich payload of proteins, RNA, and other biomolecules essential for cellular communication and repair. Typically 30–200 nanometers in size, these extracellular vesicles play a pivotal role in maintaining and restoring cellular health.
At OmniStem, we harness the therapeutic potential of exosomes derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (U-MSCs). These exosomes act as messengers, delivering regenerative signals to damaged tissues to support healing and reduce inflammation.
U-MSC stem cell treatments are considered specialized and are generally not covered by insurance plans.
U-MSC-derived allogenic stem cell therapies are currently not allowed in the U.S.
While mesenchymal stem cells (U-MSCs) have received FDA approval, the FDA does not permit the expansion of allogenic stem cells. As a result, patients undergoing these therapies in the U.S. typically receive a limited number of cells, which may reduce the potential benefits, including the use of U-MSC-derived exosomes.
At OmniStem, we use a safe and controlled laboratory process to expand these cells, enabling us to administer tens of millions of U-MSCs and U-MSC exosomes to our patients. This approach significantly enhances treatment outcomes.
This is a key reason many individuals travel to countries like Colombia, Panamá, Mexico, and the Dominican Republic to seek recognized providers of the most advanced regenerative medicine biologics available.
Our main facilities are located in the city of Pereira, in Colombia. We have specialized clinics and application centers for stem cell treatments that comply with all biosafety protocols and the highest safety standards. Pereira is the capital of the Colombian coffee region, one of the wonders of tourism in the country, and a World Heritage Site declared by UNESCO.







