Scientific Resources
Explore OmniStem’s Regenerative Medicine Library.
-
What Are Stem Cells?
-
What Are Exosomes?
-
Roles of U-MSC and Exosomes
-
Stem Cell Sourcing
-
Signature Protocols
-
Conditions Treated
-
Availability in the U.S.
-
Third Party Publications
-
F.A.Q
What Are Stem Cells?
By Dr. Yoly Castellanos | Date: AGO 20 2024
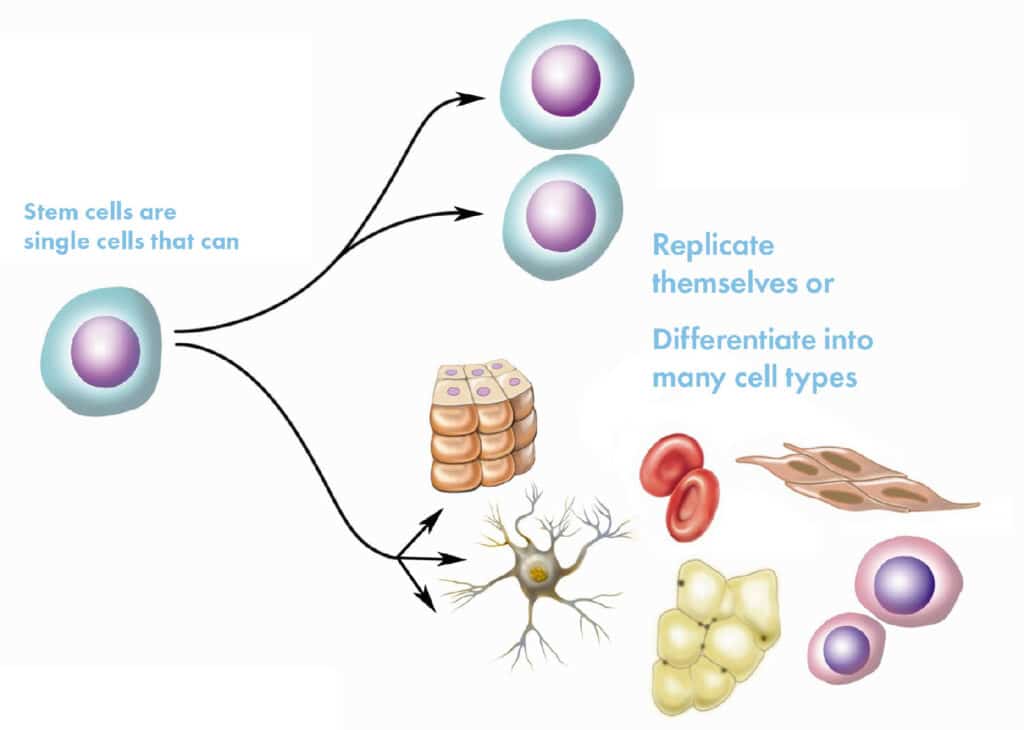
Stem cells are special cells that have the ability to transform into other types of cells in the body, such as bone, muscle, cartilage, or skin cells. Additionally, they have the ability to self-renew, meaning they can divide and produce more stem cells.
In regenerative medicine, stem cells are extremely valuable because they help repair and regenerate damaged tissues, reduce inflammation, and support the immune system.
There are different types of stem cells; for example, mesenchymal stem cells (U-MSCs) from the umbilical cord, which are young and highly versatile. These are frequently used in treatments because they have a low risk of rejection and are effective in treating chronic and degenerative conditions. These are the ones we at OmniStem use.
Key Characteristics of U-MSCs
Differentiation Capacity: U-MSCs can transform into different cell types, including osteocytes (bone cells), chondrocytes (cartilage cells), and adipocytes (fat cells), among others.
Immunomodulatory Properties: They can modulate the immune response, which is useful in treating autoimmune diseases and preventing transplant rejection.
Regenerative Ability: These cells can aid in the repair and regeneration of damaged tissues, making them promising for treating injuries and degenerative diseases.
Accessibility and Ethics: Umbilical cord stem cells are relatively easy to obtain from an umbilical cord that would otherwise be discarded after birth. Their collection does not pose significant ethical concerns, unlike embryonic stem cells.
These characteristics make U-MSCs a valuable resource in the research and treatment of a wide range of medical conditions, including neurological, cardiac, orthopedic, and autoimmune diseases.
What Are Exosomes?
By Dr. Yoly Castellanos | Date: AGO 19 2024
Exosomes are microscopic, sac-like vesicles naturally released by cells, containing a rich payload of proteins, RNA, and other biomolecules essential for cellular communication and repair. Typically 30–200 nanometers in size, these extracellular vesicles play a pivotal role in maintaining and restoring cellular health.
At OmniStem, we harness the therapeutic potential of exosomes derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (U-MSCs). These exosomes act as messengers, delivering regenerative signals to damaged tissues to support healing and reduce inflammation.
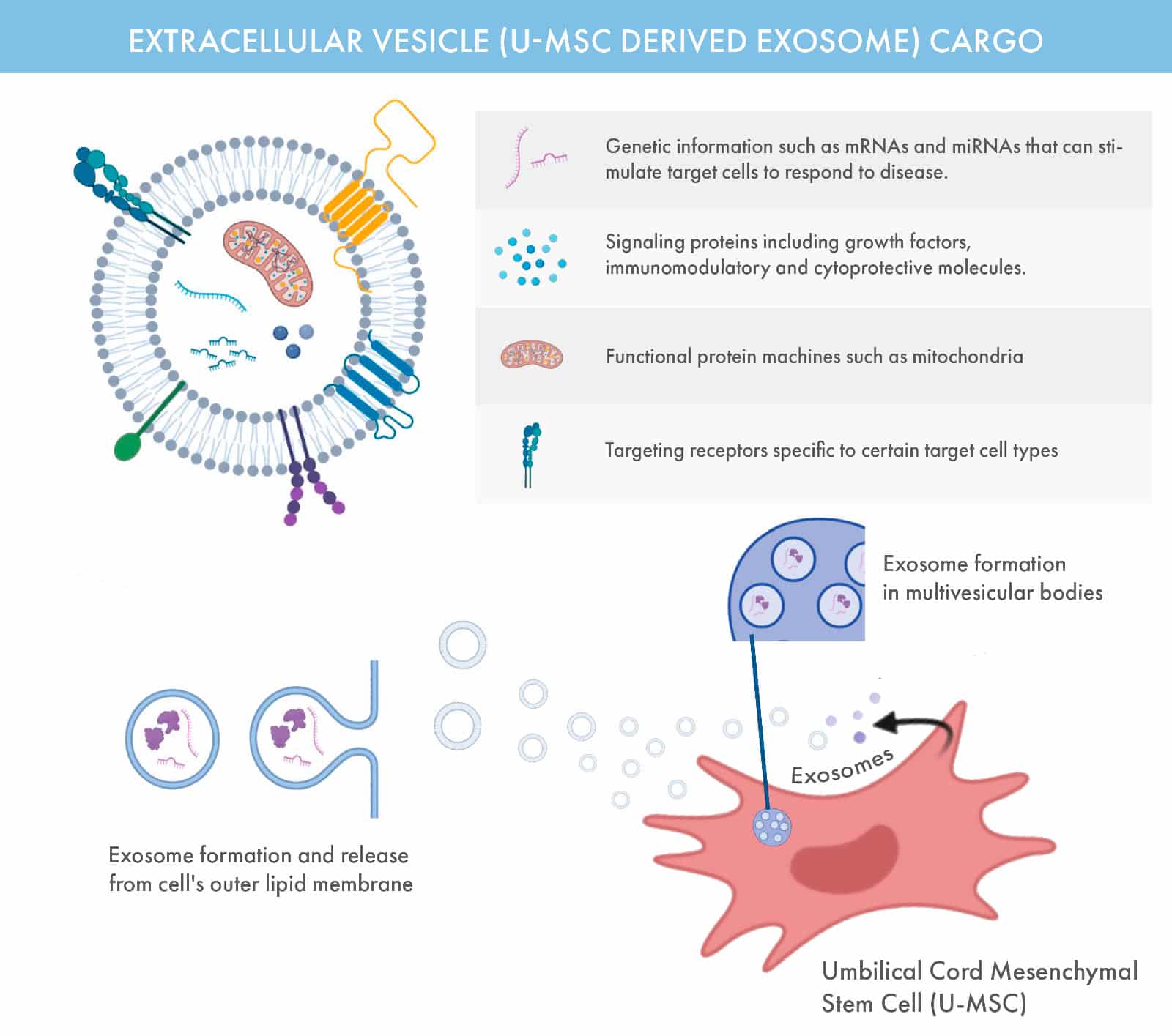
Key Roles of Exosomes
Cell-to-Cell Communication: Exosomes facilitate the transfer of biological information, enabling coordinated responses across cells.
Immune Modulation: They influence the immune system, helping balance inflammation and repair.
Regenerative Applications: Exosomes are central to treatments for skin rejuvenation, hair restoration, and advanced regenerative therapies.
Diagnostic Potential: Their contents reflect the state of their cell of origin, making them valuable tools for early detection and monitoring of conditions like cancer.
Exosomes are found in U-MSC, and their ability to reflect their originating cells makes them a promising focus for both research and clinical innovation. At OmniStem, we leverage this science to enhance the outcomes of our regenerative medicine therapies.
The Roles of U-MSCs and Exosomes
By Dr. Yoly Castellanos | Date: AGO 19 2024
Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (U-MSCs) are a type of adult stem cell harvested from Wharton’s jelly, a cell-rich tissue within the umbilical cord. These young, undifferentiated cells are multipotent, allowing them to transform into various tissue types, such as bone, cartilage, muscle, and fat.
This versatility makes them invaluable in regenerative medicine, where they play essential roles in tissue repair, inflammation reduction, and immune modulation. Containing natural growth factors, anti-inflammatory molecules, and signaling proteins, U-MSCs are effective in repairing damaged tissues and restoring immune balance, particularly in chronic or degenerative conditions.
Their low risk of rejection and inherent immunomodulatory properties make U-MSCs a safe, effective choice for reducing inflammation and promoting healing across a broad range of therapeutic applications.
Exosomes Derived from U-MSCs
Exosomes are nano-sized vesicles (30–150 nanometers) naturally secreted by U-MSCs. These cell-free particles carry bioactive molecules, including proteins, RNA, lipids, and growth factors, which function as intercellular messengers, delivering instructions that influence cellular behavior.
Unlike complete stem cells, exosomes work mainly through cell-to-cell communication instead of differentiation, enabling them to activate tissue repair, reduce inflammation, and enhance immune modulation throughout the body.
Their small size allows them lo to cross biological barriers, such as the blood-brain and nasal barriers, delivering therapeutic signals directly to target cells. This capability makes them highly effective in treating neurodegenerative diseases and modulating immune responses without the risks associated with cell-based therapies. Additionally, exosomes’ precision in targeting specific areas optimizes the body’s regenerative response, reduces immune rejection risk, and promotes anti-inflammatory healing.
Why We Use Both U-MSCs and Exosomes
Combining U-MSCs and their exosomes leverages the unique strengths of each. While U-MSCs offer direct regenerative capabilities through cell replacement and tissue repair, exosomes enhance cellular function, reduce inflammation, and promote healing without requiring full cell transplantation.
Together, U-MSCs and exosomes create a powerful, holistic approach to regenerative care, addressing both the underlying tissue damage and inflammation with precise, targeted healing.
Key Differences Between U-MSCs and Their Exosomes
Characteristic
U-MSCs
U-MSCs Derived Exosomes
Source
Derived from Wharton’s jelly in the umbilical cord, an ethically sourced, rich source of mesenchymal stem cells without harming the donor.
Nano-sized vesicles secreted by U-MSCs, carrying molecular cargo such as proteins, lipids, RNA, and growth factors.
Structure
Complete, nucleated cells with cellular organelles (e.g., mitochondria, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum) for metabolic and regenerative functions.
Small, membrane-bound vesicles (30–150 nm) lacking organelles or nucleus, acting as messengers with bioactive molecules.
Differentiation Ability
Multipotent, able to differentiate into various cell types such as bone, cartilage, muscle, and fat cells, allowing them to directly replace damaged cells.
Do not differentiate; exert therapeutic effects by signaling to resident cells, promoting healing and functional improvement.
Mechanism of Action
Integrate and proliferate within damaged tissue, differentiating into target cell types to replace or restore damaged tissues. U-MSCs also release bioactive molecules.
Facilitate intercellular communication by delivering signaling molecules directly into target cells, modulating cellular environment.
Immunomodulatory Properties
Release cytokines and growth factors that suppress pro-inflammatory responses, reduce immune cell activation, and promote T-regulatory cell growth to prevent autoimmunity.
Contain immunomodulatory molecules (e.g., anti-inflammatory cytokines, miRNAs) that interact with immune cells, reducing inflammation.
Therapeutic Applications
Effective for tissue repair and regeneration, such as in osteoarthritis, spinal conditions, and sports injuries. Ideal for conditions requiring new tissue generation.
Ideal for conditions needing immune modulation, anti-inflammatory effects, or neural protection, including neurological, autoimmune, and dermatological conditions.
Administration Methods
Typically administered intravenously or directly into target tissues (e.g., intra-articular injections for joints) to allow migration to the injury site.
Can be administered intravenously, intranasally (to reach the brain), ocularly, or in localized injections (e.g., facial skin) for targeted, high-absorption effects.
Structure
Typically administered intravenously or directly into target tissues (e.g., intra-articular injections for joints) to allow migration to the injury site.
Can be administered intravenously, intranasally (to reach the brain), ocularly, or in localized injections (e.g., facial skin) for targeted, high-absorption effects.
Blood-Brain Barrier Penetration
Limited ability to cross the BBB, restricting direct treatment of CNS diseases; their use in neurological conditions is limited to areas outside this barrier.
Can be administered intravenously, intranasally (to reach the brain), ocularly, or in localized injections (e.g., facial skin) for targeted, high-absorption effects.
Blood-Brain Barrier Penetration
Limited ability to cross the BBB, restricting direct treatment of CNS diseases; their use in neurological conditions is limited to areas outside this barrier.
Known to cross the BBB, making them effective for neurological applications like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Main Benefits
Direct tissue regeneration and repair through differentiation into specific cell types; potent anti-inflammatory properties beneficial in joint and tissue repair.
Facilitate cell signaling for enhanced tissue healing, anti-inflammatory effects, neuroprotection, skin rejuvenation, and immune regulation.
Tissue Targeting and Longevity
Can actively migrate to inflammation or injury sites; however, long-term presence depends on immune compatibility and may face rejection if not well-matched.
More versatile in tissue targeting due to their small size, with minimal immune reactions, leading to potentially longer activity in the target tissue.
Tumorigenic Risk
No known risk of uncontrolled cell growth or tumor formation; no chromosomal abnormalities, ensuring cell safety.
No tumorigenic risk, as exosomes cannot proliferate; they only influence existing cells and are rapidly metabolized, presenting a low-risk profile for cancer patients.
Anti-Aging and Aesthetic Use
Beneficial for age-related musculoskeletal decline, such as arthritis and osteoporosis, due to their regenerative capacity.
Widely used in anti-aging and cosmetic treatments (e.g., skin rejuvenation, hair growth) due to collagen stimulation and cellular renewal without invasive procedures.
Conclusion
Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (U-MSCs) and their exosomes offer complementary advantages in regenerative medicine. By combining the direct tissue repair abilities of U-MSCs with the targeted anti-inflammatory and signaling effects of exosomes.
Sources:
1. Therapeutic Application of Exosomes in Inflammatory Diseases – PMC (nih.gov)
2. Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes on Autoimmune Diseases – PMC (nih.gov) *
3. Human adipose mesenchymal stem cells modulate inflammation and angiogenesis through exosomes | Scientific Reports (nature.com)
4. The Effect of miRNA-Modified Exosomes in Animal Models of Spinal Cord Injury: A meta-Analysis – PMC (nih.gov)
5. JCI Insight – Exosomes from mesenchymal stromal cells reduce murine colonic inflammation via a macrophage-dependent mechanism
6. Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes Alleviate Acute Lung Injury by Inhibiting Alveolar Macrophage Pyroptosis | Stem Cells Translational Medicine | Oxford Academic (oup.com)
7. Therapeutic role of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in respiratory disease | Stem Cell Research & Therapy | Full Text (biomedcentral.com)
How are our U-MSC and derived exosomes sourced?
At OmniStem we source our umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and U-MSC derived exosomes through a collaborative partnership with the National University in Medellín, Colombia. We work closely with a skilled team of biotechnologists and a fertility clinic, which provides us with donated umbilical cords.
The harvesting and preservation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (U-MSCs) is a delicate and highly technical procedure carried out in three phases to ensure the viability and effectiveness of the cells for therapeutic applications.
Suitability
This stage involves a comprehensive evaluation of umbilical cord donors, which includes DNA and laboratory analyses to ensure the integrity and viability of the U-MSC stem cells obtained.
Harvesting and Preservation
This phase emphasizes the collection and preservation of the umbilical cord, typically discarded postpartum and the extraction and laboratory expansion of multipotent cells and their derived exosomes.
Expansion and Testing
The stem cells used for therapeutic applications are verified by a third party lab and expanded in our laboratory, in this phase we process the extraction the U-MSC derived exosomes.
Our team in Colombia produces some of the highest-quality biologics available globally. While similar work is conducted in countries like South Korea, China, and Russia, our focus is distinct in emphasizing both exosome and mesenchymal U-MSC therapies.

Our Signature Protocols
Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell (U-MSC) and derived exosome therapies are the cornerstone of regenerative medicine, offering a new treatment approach for various medical conditions and diseases where treatment options are limited.
The use of biological products derived from U-MSC obtained from Wharton's gelatin (mesenchymal cells and exosomes derived from the umbilical cord) improve organ function, exert immunomodulatory effects, repair, regenerate and anti-inflammatory effect of affected tissues in the entire system, while exhibiting an exemplary safety profile.
The StemSpine® protocol targets injured vertebral structures by directly applying biologics derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (U-MSCs). This approach aims to deliver immunomodulatory, reparative, regenerative, and anti-inflammatory effects to the affected areas, such as intervertebral discs or vertebrae, enhancing healing and improving spine conditions.
Joint injections entail the targeted application of biologics derived from U-MSC stem cells to injured joints. The biological product is deposited directly at the site of the injury (such as the tendon, joint, or joint capsule), enabling immunomodulatory, reparative, regenerative, and anti-inflammatory effects.
The Stem Grow treatment targets both halting hair loss and enhancing the quality and thickness of the hair. Utilizing biological products derived from U-MSC, it aims to regenerate hair, counteract pathological mechanisms contributing to hair loss, and stimulate damaged hair follicles. This treatment entails the subdermal application of exosomes to the scalp.
Is This Therapy Available in the U.S.?
U-MSC-derived allogenic stem cell therapies are currently not allowed in the U.S.
While mesenchymal stem cells (U-MSCs) have received FDA approval, the FDA does not permit the expansion of allogenic stem cells. As a result, patients undergoing these therapies in the U.S. typically receive a limited number of cells, which may reduce the potential benefits, including the use of U-MSC-derived exosomes.
At OmniStem, we use a safe and controlled laboratory process to expand these cells, enabling us to administer tens of millions of U-MSCs and U-MSC exosomes to our patients. This approach significantly enhances treatment outcomes.
This is a key reason many individuals travel to countries like Colombia, Panama, Mexico, and the Dominican Republic to seek recognized providers of the most advanced regenerative medicine biologics available.
OmniStem
Wellness Retreats
Join us at OmniStem to experience a pioneering approach to regenerative medicine tailored specifically to your personal health needs. Discover how you can rejuvenate your body through Umbilical Cord Stem Cell and Exosome therapies.
Find Out if You Are
Candidate for Treatment
To determine if you are a suitable candidate for this treatment, please complete our Pre-screening Questionnaire. Our team of medical team will assess your eligibility based on your health status and medical history.
Third Party Scientific Publications
Explore scientific publications organized by condition to gain insights into the outcomes of umbilical cord stem cell and exosome therapies.
• U-MSC Derived Exosomes
• Anti-Aging and Wellness
• Neurological Conditions
• Autism Spectrum Disorder
• Spine Conditions
• Autoimmune Disorders
• Sports Injuries
• Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
• Pulmonary Disease
• Intervertebral Disc Regeneration
• Multiple Sclerosis
• Hair loss and Alopecia
• Joint Conditions
• Rheumatoid Arthriti
Hadanny, Amir; Sasson, Efrat; Copel, Laurian; Daniel-Kotovsky, Malka; Yaakobi, Eldad; Lang, Erez; Fishlev, Gregory; Polak, Nir; Friedman, Mony; Doenyas, Keren; Finci, Shachar; Zemel, Yonatan; Bechor, Yair; Efrati, Shai
Physical enhancement of older adults using hyperbaric oxygen: a randomized controlled trial Journal Article
In: 2024.
@article{nokey,
title = {Physical enhancement of older adults using hyperbaric oxygen: a randomized controlled trial},
author = {Amir Hadanny and Efrat Sasson and Laurian Copel and Malka Daniel-Kotovsky and Eldad Yaakobi and Erez Lang and Gregory Fishlev and Nir Polak and Mony Friedman and Keren Doenyas and Shachar Finci and Yonatan Zemel and Yair Bechor and Shai Efrati},
url = {https://bmcgeriatr.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12877-024-05146-3},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-07-23},
urldate = {2024-07-23},
abstract = {Aging is associated with a progressive decline in the capacity for physical activity. The objective of the current study was to evaluate the effect of an intermittent hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) protocol on maximal physical performance and cardiac perfusion in sedentary older adults.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
M, Gupta; J, Rathored
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: future prospects in regenerative therapy and anti-aging Journal Article
In: 2024.
@article{nokey,
title = {Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: future prospects in regenerative therapy and anti-aging},
author = {Gupta M and Rathored J},
url = {https://europepmc.org/article/MED/38757145},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-05-02},
abstract = {Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) utilizes 100% oxygen at high atmospheric pressure for clinical applications. HBOT has proven to be an effective supplementary treatment for a variety of clinical and pathological disorders. HBOT's therapeutic results are based on the physiological effects of increased tissue oxygenation, or improved oxygen bioavailability. HBOT's current indications in illnesses like as wound healing, thermal or radiation burns, and tissue necrosis point to its function in facilitating the regeneration process. Various research has revealed that HBOT plays a function in vascularization, angiogenesis, and collagen production augmentation. Individual regeneration capacity is influenced by both environmental and genetic factors. Furthermore, the regenerating ability of different types of tissues varies, and this ability declines with age. HBOT affects physiological processes at the genetic level by altering gene expression, delaying cell senescence, and assisting in telomere length enhancement. The positive results in a variety of indications, ranging from tissue regeneration to better cognitive function, indicate that it has enormous potential in regenerative and anti-aging therapy.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Fernández, Olga Sonia León; Oru, Gabriel Takon; Viebahn-Haensler, Renate; Cabreja, Gilberto López; Espinosa, Irainis Serrano; Vázquez, María Elena Corrales
Medical Ozone: A Redox Regulator with Selectivity for Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Journal Article
In: 2024.
@article{nokey,
title = {Medical Ozone: A Redox Regulator with Selectivity for Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients},
author = {Olga Sonia León Fernández and Gabriel Takon Oru and Renate Viebahn-Haensler and Gilberto López Cabreja and Irainis Serrano Espinosa and María Elena Corrales Vázquez},
url = {https://europepmc.org/article/MED/38543177},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-03-19},
abstract = {Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA) are the most common arthritic diseases. Medical ozone has demonstrated its effectiveness in combination therapy with methotrexate or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for RA and OA, respectively. Although RA and OA have been compared from different points of view, few studies have considered their redox status in spite of the oxidative processes that are involved in both diseases. The aim of this study was to compare RA with OA, evaluating their redox status and the effects of ozone on their clinical response to combined therapy with ozone. The redox status of 80 patients was determined: antioxidant defenses, injury markers, two subjective variables (pain and disability), and levels of antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptides were evaluated. Oxidative stress and clinical response to combined therapy with ozone was higher than in the case of RA. After medical ozone treatment, there was an increase in antioxidant defense and a decrease in injury markers as well as pain, disability, and autoantibody concentrations. Redox biomarkers were able to differentiate between both arthritic diseases and combined therapy with ozone (methotrexate + ozone), showing a therapeutic selectivity for RA in comparison with OA.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Chirumbolo, Salvatore; Valdenassi, Luigi; Tirelli, Umberto; Ricevuti, Giovanni; Pandolfi, Sergio; Vaiano, Francesco; Galoforo, Antonio; Loprete, Fortunato; Simonetti, Vincenzo; Chierchia, Marianna; Bellardi, Debora; Richelmi, Tommaso; Franzini, Marianno
How Ozone Applications in the Blood Can Influence Clinical Therapy Success via the Modulation of Cell Biology and Immunity Journal Article
In: 2023.
@article{nokey,
title = {How Ozone Applications in the Blood Can Influence Clinical Therapy Success via the Modulation of Cell Biology and Immunity},
author = {Salvatore Chirumbolo and Luigi Valdenassi and Umberto Tirelli and Giovanni Ricevuti and Sergio Pandolfi and Francesco Vaiano and Antonio Galoforo and Fortunato Loprete and Vincenzo Simonetti and Marianna Chierchia and Debora Bellardi and Tommaso Richelmi and Marianno Franzini},
url = {https://www.mdpi.com/2079-7737/12/12/1512},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-12-11},
abstract = {Background. Ozone is an allotrope of oxygen whose use in medicine has rapidly grown in recent years. Ozonated blood allows for the use of ozone in a safe modality, as plasma and blood cells are endowed with an antioxidant system able to quench ozone’s pro-oxidant property and to elicit the Nrf2/Kwap1/ARE pathway. Methods. We present two clinical studies, a case-series (six patients) observational study adopting ozone as a major autohemotherapy and topical ozone to address infected post-surgical wounds with multi-drug resistant bacteria and an observational study (250 patients) using ozonated blood for treating knee osteoarthritis. Results. Ozonated blood via major autohemotherapy reduced the extent of infections in wounds, reduced the inflammatory biomarkers by more than 75% and improved patients’ QoL, whereas ozonated blood via minor autohemotherapy improved significantly (p < 0.001) WOMAC and Lequesne’s parameters in knee osteoarthritis. Conclusions. The models described, i.e., ozone autohemotherapy in wound antimicrobial treatment and ozonated blood in knee osteoarthrosis, following our protocols, share the outstanding ability of ozone to modulate the innate immune response and address bacterial clearance as well as inflammation and pain.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Tran, Dang-Khoa; Nguyen, Thuy; Phuong, Thi; Bui, Nhat-Le; Singh, Vijai; Looi, Qi Hao
Exploring the Potential of Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Aesthetic and Plastic Surgery Journal Article
In: 2023.
@article{nokey,
title = {Exploring the Potential of Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Aesthetic and Plastic Surgery},
author = {Dang-Khoa Tran and Thuy Nguyen and Thi Phuong and Nhat-Le Bui and Vijai Singh and Qi Hao Looi},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1109/RBME.2021.3134994},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1109/RBME.2021.3134994},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-01-05},
urldate = {2023-01-05},
abstract = {Over the last decade, stem cell-associated therapies are widely used because of their potential in self-renewable and multipotent differentiation ability. Stem cells have become more attractive for aesthetic uses and plastic surgery, including scar reduction, breast augmentation, facial contouring, hand rejuvenation, and anti-aging. The current preclinical and clinical studies of stem cells on aesthetic uses also showed promising outcomes. Adipose-derived stem cells are commonly used for fat grafting that demonstrated scar improvement, anti-aging, skin rejuvenation properties, etc. While stem cell-based products have yet to receive approval from the FDA for aesthetic medicine and plastic surgery. Moving forward, the review on the efficacy and potential of stem cell-based therapy for aesthetic and plastic surgery is limited. In the present review, we discuss the current status and recent advances of using stem cells for aesthetic and plastic surgery. The potential of cell-free therapy and tissue engineering in this field is also highlighted. The clinical applications, advantages, and limitations are also discussed. This review also provides further works that need to be investigated to widely apply stem cells in the clinic, especially in aesthetic and plastic contexts.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
B, Bhujel; HE, Shin; DJ, Choi; I, Han
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Intervertebral Disc Regeneration Review Journal Article
In: 2022.
@article{nokey,
title = {Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Intervertebral Disc Regeneration Review},
author = {Bhujel B and Shin HE and Choi DJ and Han I},
url = {https://europepmc.org/article/MED/35806304},
doi = {https://europepmc.org/article/MED/35806304},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-06-30},
urldate = {2022-06-30},
abstract = {Intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD) is a common cause of lower back pain (LBP), which burdens individuals and society as a whole. IVDD occurs as a result of aging, mechanical trauma, lifestyle factors, and certain genetic abnormalities, leads to loss of nucleus pulposus, alteration in the composition of the extracellular matrix, excessive oxidative stress, and inflammation in the intervertebral disc. Pharmacological and surgical interventions are considered a boon for the treatment of IVDD, but the effectiveness of those strategies is limited. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have recently emerged as a possible promising regenerative therapy for IVDD due to their paracrine effect, restoration of the degenerated cells, and capacity for differentiation into disc cells. Recent investigations have shown that the pleiotropic effect of MSCs is not related to differentiation capacity but is mediated by the secretion of soluble paracrine factors. Early studies have demonstrated that MSC-derived exosomes have therapeutic potential for treating IVDD by promoting cell proliferation, tissue regeneration, modulation of the inflammatory response, and reduced apoptosis. This paper highlights the current state of MSC-derived exosomes in the field of treatment of IVDD with further possible future developments, applications, and challenges.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Wang, Hao-Nan; Rong, Xiao; Yang, Lu-Ming; Hua, Wei-Zhong; Nicorresponding, Guo-Xin
Advances in Stem Cell Therapies for Rotator Cuff Injuries Journal Article
In: 2022.
@article{nokey,
title = {Advances in Stem Cell Therapies for Rotator Cuff Injuries},
author = {Hao-Nan Wang and Xiao Rong and Lu-Ming Yang and Wei-Zhong Hua and Guo-Xin Nicorresponding},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9174670/},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-05-25},
abstract = {Rotator cuff injury is a common upper extremity musculoskeletal disease that may lead to persistent pain and functional impairment. Despite the clinical outcomes of the surgical procedures being satisfactory, the repair of the rotator cuff remains problematic, such as through failure of healing, adhesion formation, and fatty infiltration. Stem cells have high proliferation, strong paracrine action, and multiple differentiation potential, which promote tendon remodeling and fibrocartilage formation and increase biomechanical strength. Additionally, stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) can increase collagen synthesis and inhibit inflammation and adhesion formation by carrying regulatory proteins and microRNAs. Therefore, stem cell-based therapy is a promising therapeutic strategy that has great potential for rotator cuff healing. In this review, we summarize the advances of stem cells and stem cell-derived EVs in rotator cuff repair and highlight the underlying mechanism of stem cells and stem cell-derived EVs and biomaterial delivery systems. Future studies need to explore stem cell therapy in combination with cellular factors, gene therapy, and novel biomaterial delivery systems.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Ding, Guocheng; Du, Jianing; Hu, Xiaoqing; Yingfang,
Mesenchymal Stem Cells From Different Sources in Meniscus Repair and Regeneration Journal Article
In: 2022.
@article{nokey,
title = {Mesenchymal Stem Cells From Different Sources in Meniscus Repair and Regeneration},
author = {Guocheng Ding and Jianing Du and Xiaoqing Hu and Yingfang},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9091333/},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-04-27},
urldate = {2022-04-27},
abstract = {Meniscus damage is a common trauma that often arises from sports injuries or menisci tissue degeneration. Current treatment methods focus on the repair, replacement, and regeneration of the meniscus to restore its original function. The advance of tissue engineering provides a novel approach to restore the unique structure of the meniscus. Recently, mesenchymal stem cells found in tissues including bone marrow, peripheral blood, fat, and articular cavity synovium have shown specific advantages in meniscus repair. Although various studies explore the use of stem cells in repairing meniscal injuries from different sources and demonstrate their potential for chondrogenic differentiation, their meniscal cartilage-forming properties are yet to be systematically compared. Therefore, this review aims to summarize and compare different sources of mesenchymal stem cells for meniscal repair and regeneration.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Kebria, Maziar Malekzadeh; Milan, Peiman Brouki; Peyravian, Noshad; Kiani, Jafar; Khatibi, Soheil; Mozafari, Masoud
Stem cell therapy for COVID-19 pneumonia Journal Article
In: 2022.
@article{nokey,
title = {Stem cell therapy for COVID-19 pneumonia},
author = {Maziar Malekzadeh Kebria and Peiman Brouki Milan and Noshad Peyravian and Jafar Kiani and Soheil Khatibi and Masoud Mozafari},
url = {https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s43556-021-00067-8},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-02-17},
urldate = {2022-02-17},
abstract = {Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus is a highly contagious microorganism, and despite substantial investigation, no progress has been achieved in treating post-COVID complications. However, the virus has made various mutations and has spread around the world. Researchers have tried different treatments to reduce the side effects of the COVID-19 symptoms. One of the most common and effective treatments now used is steroid therapy to reduce the complications of this disease. Long-term steroid therapy for chronic inflammation following COVID-19 is harmful and increases the risk of secondary infection, and effective treatment remains challenging owing to fibrosis and severe inflammation and infection. Sometimes our immune system can severely damage ourselves in disease. In the past, many researchers have conducted various studies on the immunomodulatory properties of stem cells. This property of stem cells led them to modulate the immune system of autoimmune diseases like diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and Parkinson's. Because of their immunomodulatory properties, stem cell-based therapy employing mesenchymal or hematopoietic stem cells may be a viable alternative treatment option in some patients. By priming the immune system and providing cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors, stem cells can be employed to build a long-term regenerative and protective response. This review addresses the latest trends and rapid progress in stem cell treatment for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) following COVID-19.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Shi, Lei; Yuan, Xin; Yao, Weiqi; Wang, Siyu; Zhang, Chao; Zhang, Bo; Song, Jinwen; Huang, Lei; Xu, Zhe
Human mesenchymal stem cells treatment for severe COVID-19 Journal Article
In: 2021.
@article{nokey,
title = {Human mesenchymal stem cells treatment for severe COVID-19},
author = {Lei Shi and Xin Yuan and Weiqi Yao and Siyu Wang and Chao Zhang and Bo Zhang and Jinwen Song and Lei Huang and Zhe Xu},
url = {https://www.thelancet.com/journals/ebiom/article/PIIS2352-3964(21)00583-1/fulltext},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-12-25},
abstract = {The long-term consequences of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell (UC-MSC) treatment for COVID-19 patients are yet to be reported. This study assessed the 1-year outcomes in patients with severe COVID-19, who were recruited in our previous UC-MSC clinical trial.
Methods
In this prospective, longitudinal, cohort study, 100 patients enrolled in our phase 2 trial were prospectively followed up at 3-month intervals for 1 year to evaluate the long-term safety and effectiveness of UC-MSC treatment. The primary endpoint was an altered proportion of whole-lung lesion volumes measured by high-resolution CT. Other imaging outcomes, 6 min walking distance (6-MWD), lung function, plasma biomarkers, and adverse events were also recorded and analyzed. This trial was registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04288102).
Findings
MSC administration improved in whole-lung lesion volume compared with the placebo with a difference of −10.8% (95% CI: −20.7%, −1.5%, p = 0.030) on day 10. MSC also reduced the proportion of solid component lesion volume compared with the placebo at each follow-up point. More interestingly, 17.9% (10/56) of patients in the MSC group had normal CT images at month 12, but none in the placebo group (p = 0.013). The incidence of symptoms was lower in the MSC group than in the placebo group at each follow-up time. Neutralizing antibodies were all positive, with a similar median inhibition rate (61.6% vs. 67.6%) in both groups at month 12. No difference in adverse events at the 1-year follow-up and tumor markers at month 12 were observed between the two groups.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Methods
In this prospective, longitudinal, cohort study, 100 patients enrolled in our phase 2 trial were prospectively followed up at 3-month intervals for 1 year to evaluate the long-term safety and effectiveness of UC-MSC treatment. The primary endpoint was an altered proportion of whole-lung lesion volumes measured by high-resolution CT. Other imaging outcomes, 6 min walking distance (6-MWD), lung function, plasma biomarkers, and adverse events were also recorded and analyzed. This trial was registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04288102).
Findings
MSC administration improved in whole-lung lesion volume compared with the placebo with a difference of −10.8% (95% CI: −20.7%, −1.5%, p = 0.030) on day 10. MSC also reduced the proportion of solid component lesion volume compared with the placebo at each follow-up point. More interestingly, 17.9% (10/56) of patients in the MSC group had normal CT images at month 12, but none in the placebo group (p = 0.013). The incidence of symptoms was lower in the MSC group than in the placebo group at each follow-up time. Neutralizing antibodies were all positive, with a similar median inhibition rate (61.6% vs. 67.6%) in both groups at month 12. No difference in adverse events at the 1-year follow-up and tumor markers at month 12 were observed between the two groups.
A, Hadanny; R, Forer; D, Volodarsky; M, Daniel-Kotovsky; M, Catalogna; Y, Zemel; Y, Bechor; and Efrati S.,
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy induces transcriptome changes in elderly: a prospective trial. Journal Article
In: 2021.
@article{nokey,
title = {Hyperbaric oxygen therapy induces transcriptome changes in elderly: a prospective trial.},
author = {Hadanny A and Forer R and Volodarsky D and Daniel-Kotovsky M and Catalogna M and Zemel Y and Bechor Y and and Efrati S.},
url = {https://europepmc.org/article/MED/34818212},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-11-24},
abstract = {Aging is characterized by the progressive loss of physiological capacity. Changes in gene expression can alter activity in defined age-related molecular pathways leading to cellular aging and increased aging disease susceptibility. The aim of the current study was to evaluate whether hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) affects gene expression in normal, non-pathological, aging adults.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Arjmand, Babak; Roudsari, Peyvand Parhizkar; Alavi-Moghadam, Sepideh; Rezaei-Tavirani, Mostafa; Tayanloo-Beik, Akram; Mehrdad, Neda; Adibi, Hossein; Larijani, Bagher
Potential for Stem Cell-Based Therapy in the Road of Treatment for Neurological Disorders Secondary to COVID-19 Journal Article
In: 2021.
@article{nokey,
title = {Potential for Stem Cell-Based Therapy in the Road of Treatment for Neurological Disorders Secondary to COVID-19},
author = {Babak Arjmand and Peyvand Parhizkar Roudsari and Sepideh Alavi-Moghadam and Mostafa Rezaei-Tavirani and Akram Tayanloo-Beik and Neda Mehrdad and Hossein Adibi and Bagher Larijani },
url = {https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40883-021-00234-x},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-10-29},
abstract = {The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has led to the worldwide pandemic named coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). It has caused a significant increase in the number of cases and mortalities since its first diagnosis in December 2019. Although COVID-19 primarily affects the respiratory system, neurological involvement of the central and peripheral nervous system has been also reported. Herein, the higher risk of neurodegenerative diseases in COVID-19 patients in future is also imaginable. Neurological complications of COVID-19 infection are more commonly seen in severely ill individuals; but, earlier diagnosis and treatment can lead to better long-lasting results. In this respect, stem cell biotechnologies with considerable self-renewal and differentiation capacities have experienced great progress in the field of neurological disorders whether in finding out their underlying processes or proving them promising therapeutic approaches. Herein, many neurological disorders have been found to benefit from stem cell medicine strategies. Accordingly, in the present review, the authors are trying to discuss stem cell-based biotechnologies as promising therapeutic options for neurological disorders secondary to COVID-19 infection through reviewing neurological manifestations of COVID-19 and current stem cell-based biotechnologies for neurological disorders.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
X, Xiao; M, Xu; H, Yu; L, Wang; X, Li; J, Rak; S, Wang; RC, Zhao
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Mitigate Oxidative Stress-induced Senescence in Endothelial Cells Journal Article
In: 2021.
@article{nokey,
title = {Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Mitigate Oxidative Stress-induced Senescence in Endothelial Cells},
author = {Xiao X and Xu M and Yu H and Wang L and Li X and Rak J and Wang S and Zhao RC},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-021-00765-3},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-021-00765-3},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-10-21},
urldate = {2021-10-21},
abstract = {Senescent endothelial cells (ECs) could impair the integrity of the blood vessel endothelium, leading to vascular aging and a series of diseases, such as atherosclerosis, diabetes. Preventing or mitigating EC senescence might serve as a promising therapeutic paradigm for these diseases. Recent studies showed that small extracellular vesicles (sEV) have the potential to transfer bioactive molecules into recipient cells and induce phenotypic changes. Since mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have long been postulated as an important source cell in regenerative medicine, herein we investigated the role and mechanism of MSC-derived sEV (MSC-sEV) on EC senescence. In vitro results showed that MSC-sEV reduced senescent biomarkers, decreased senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP), rescued angiogenesis, migration and other dysfunctions in senescent EC induced by oxidative stress. In the In vivo natural aging and type-2 diabetes mouse wound-healing models (both of which have senescent ECs), MSC-sEV promoted wound closure and new blood vessel formation. Mechanically, miRNA microarray showed that miR-146a was highly expressed in MSC-sEV and also upregulated in EC after MSC-sEV treatment. miR-146a inhibitors abolished the stimulatory effects of MSC-sEV on senescence. Moreover, we found miR-146a could suppress Src phosphorylation and downstream targets VE-cadherin and Caveolin-1. Collectively, our data indicate that MSC-sEV mitigated endothelial cell senescence and stimulate angiogenesis through miR-146a/Src.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Shen, Ziwei; Huang, Wei; Liu, Jun; Tian, Jie; Wang, Shengjun; Rui, Ke
Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes on Autoimmune Diseases Journal Article
In: 2021.
@article{nokey,
title = {Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes on Autoimmune Diseases},
author = {Ziwei Shen and Wei Huang and Jun Liu and Jie Tian and Shengjun Wang and Ke Rui},
url = {https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.749192},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-09-21},
urldate = {2021-09-21},
abstract = {Recent years, the immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been demonstrated in preclinical studies and trials of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Emerging evidence indicates that the immunomodulatory effect of MSCs is primarily attributed to the paracrine pathway. As one of the key paracrine effectors, mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (MSC-EXOs) are small vesicles 30-200 nm in diameter that play an important role in cell-to-cell communication by carrying bioactive substances from parental cells. Recent studies support the finding that MSC-EXOs have an obvious inhibitory effect toward different effector cells involved in the innate and adaptive immune response. Moreover, substantial progress has been made in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, including multiple sclerosis (MS), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), type-1 diabetes (T1DM), uveitis, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). MSC-EXOs are capable of reproducing MSC function and overcoming the limitations of traditional cell therapy. Therefore, using MSC-EXOs instead of MSCs to treat autoimmune diseases appears to be a promising cell-free treatment strategy. In this review, we review the current understanding of MSC-EXOs and discuss the regulatory role of MSC-EXOs on immune cells and its potential application in autoimmune diseases.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Shen, Ziwei; Huang, Wei; Liu, Jun; Tian, Jie; Wang, Shengjun; Rui, Ke
Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes on Autoimmune Diseases Journal Article
In: 2021.
@article{nokey,
title = {Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes on Autoimmune Diseases},
author = {Ziwei Shen and Wei Huang and Jun Liu and Jie Tian and Shengjun Wang and Ke Rui},
url = {https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.749192},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-09-21},
urldate = {2021-09-21},
abstract = {Recent years, the immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been demonstrated in preclinical studies and trials of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Emerging evidence indicates that the immunomodulatory effect of MSCs is primarily attributed to the paracrine pathway. As one of the key paracrine effectors, mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (MSC-EXOs) are small vesicles 30-200 nm in diameter that play an important role in cell-to-cell communication by carrying bioactive substances from parental cells. Recent studies support the finding that MSC-EXOs have an obvious inhibitory effect toward different effector cells involved in the innate and adaptive immune response. Moreover, substantial progress has been made in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, including multiple sclerosis (MS), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), type-1 diabetes (T1DM), uveitis, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). MSC-EXOs are capable of reproducing MSC function and overcoming the limitations of traditional cell therapy. Therefore, using MSC-EXOs instead of MSCs to treat autoimmune diseases appears to be a promising cell-free treatment strategy. In this review, we review the current understanding of MSC-EXOs and discuss the regulatory role of MSC-EXOs on immune cells and its potential application in autoimmune diseases.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Stewart, Claire E.
Stem cells and regenerative medicine in sport science Journal Article
In: 2021.
@article{nokey,
title = {Stem cells and regenerative medicine in sport science},
author = {Claire E. Stewart},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-08-27},
abstract = {The estimated cost of acute injuries in college-level sports in the USA is ∼1.5 billion dollars annually, without considering the cost of follow-up rehabilitation. In addition to this huge financial burden, sports injuries may be career-ending for some athletes without appropriate diagnosis and relevant interventions. With a growing number of females participating in contact-based and pivoting sports, middle-aged individuals returning to sports,s and natural injuries of aging all increasing, such costs and negative implications for quality of life will expand. For those injuries that cannot be predicted and prevented, there is a real need to optimize repair, recovery, and function post-injury in the sporting and clinical worlds. The 21st century has seen rapid growth in regenerative medicine for sporting injuries to progress recovery and facilitate return to sport. Such interventions harness knowledge relating to stem cells as a potential for injury repair. While the field is rapidly growing, consideration beyond the stem cells to the factors they secrete should be considered in developing practical, affordable treatments.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Krut, Zoe; Pelled, Gadi; Gazit, Dan; Gazit, Zulma
Stem Cells and Exosomes: New Therapies for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Journal Article
In: 2021.
@article{nokey,
title = {Stem Cells and Exosomes: New Therapies for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration},
author = {Zoe Krut and Gadi Pelled and Dan Gazit and Zulma Gazit},
url = {https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092241},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092241},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-08-20},
urldate = {2021-08-20},
abstract = {Intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD) occurs as a result of an imxbalance of the anabolic and catabolic processes in the intervertebral disc, leading to an alteration in the composition of the extracellular matrix (ECM), loss of nucleus pulposus (NP) cells, excessive oxidative stress and inflammation. Degeneration of the IVD occurs naturally with age, but mechanical trauma, lifestyle factors and certain genetic abnormalities can increase the likelihood of symptomatic disease progression. IVDD, often referred to as degenerative disc disease (DDD), poses an increasingly substantial financial burden due to the aging population and increasing incidence of obesity in the United States. Current treatments for IVDD include pharmacological and surgical interventions, but these lack the ability to stop the progression of disease and restore the functionality of the IVD. Biological therapies have been evaluated but show varying degrees of efficacy in reversing disc degeneration long-term. Stem cell-based therapies have shown promising results in the regeneration of the IVD, but face both biological and ethical limitations. Exosomes play an important role in intercellular communication, and stem cell-derived exosomes have been shown to maintain the therapeutic benefit of their origin cells without the associated risks. This review highlights the current state of research on the use of stem-cell derived exosomes in the treatment of IVDD.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Xu, Yue; Zhang, Wan-Xia; Wang, Li-Na; Ming, Yue-Qing; Li, Yu-Lin; Ni, Guo-Xin
Stem cell therapies in tendon-bone healing Journal Article
In: 2021.
@article{nokey,
title = {Stem cell therapies in tendon-bone healing},
author = {Yue Xu and Wan-Xia Zhang and Li-Na Wang and Yue-Qing Ming and Yu-Lin Li and Guo-Xin Ni},
url = {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8316867/},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-07-26},
abstract = {Tendon-bone insertion injuries such as rotator cuff and anterior cruciate ligament injuries are currently highly common and severe. The key method of treating this kind of injury is the reconstruction operation. The success of this reconstructive process depends on the ability of the graft to incorporate into the bone. Recently, there has been substantial discussion about how to enhance the integration of tendon and bone through biological methods. Stem cells like bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), tendon stem/progenitor cells, synovium-derived MSCs, adipose-derived stem cells, or periosteum-derived periosteal stem cells can self-regenerate and potentially differentiate into different cell types, which have been widely used in tissue repair and regeneration. Thus, we concentrate in this review on the current circumstances of tendon-bone healing using stem cell therapy.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Y, Hachmo; A, Hadanny; R, Abu Hamed; M, Daniel-Kotovsky; M, Catalogna; G, Fishlev; E, Lang; N, Polak; K, Doenyas; M, Friedman; Y, Zemel; Y, Bechor; S., Efrati
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy increases telomere length and decreases immunosenescence in isolated blood cells Journal Article
In: 2020.
@article{nokey,
title = {Hyperbaric oxygen therapy increases telomere length and decreases immunosenescence in isolated blood cells},
author = {Hachmo Y and Hadanny A and Abu Hamed R and Daniel-Kotovsky M and Catalogna M and Fishlev G and Lang E and Polak N and Doenyas K and Friedman M and Zemel Y and Bechor Y and Efrati S.},
url = {https://europepmc.org/article/MED/33206062},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-11-18},
abstract = {Aging is characterized by the progressive loss of physiological capacity. At the cellular level, two key hallmarks of the aging process include telomere length (TL) shortening and cellular senescence. Repeated intermittent hyperoxic exposures, using certain hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) protocols, can induce regenerative effects which normally occur during hypoxia. The aim of the current study was to evaluate whether HBOT affects TL and senescent cell concentrations in a normal, non-pathological, aging adult population.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Yuan, An-Ran; Bian, Qiong; Gao, Jian-Qing
Current advances in stem cell-based therapies for hair regeneration Journal Article
In: 2020.
@article{nokey,
title = {Current advances in stem cell-based therapies for hair regeneration},
author = {An-Ran Yuan and Qiong Bian and Jian-Qing Gao},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173197},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-08-15},
abstract = {Alopecia is resulted from various factors that can decrease the regeneration capability of hair follicles and affect hair cycles. This process can be devastating physically and psychologically. Nevertheless, the available treatment strategies are limited, and the therapeutic outcomes are not satisfactory. According to the possible pathogenesis of nonscarring alopecia, especially androgenetic alopecia, recovering or replenishing the signals responsible for hair follicle stem cells activation is a promising strategy for hair regeneration. Recently, stem cell-based therapies, especially those based on the stem cell-derived conditioned medium (CM), which is secreted by stem cells and is rich in paracrine factors, have been widely explored as the hair regenerative medicine. Several studies have focused on altering the composition and up-regulating the amount of secretome of the stem cells, thereby enhancing its therapeutic effects. Besides, stem cell-derived exosomes, which are present in the CM as message entities, are also promising for hair regrowth. In this review, the up-to-date progress of research efforts focused on stem cell-based therapies for hair regeneration will be discussed, including their therapeutic potentials with respective merits and demerits, as well as the possible mechanisms.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Frecuently Asked Questions
Empowering Patients Through Knowledge: This FAQ section is designed to provide clear and concise answers to the most common questions, covering everything from the fundamentals of stem cell therapy to the specifics of our treatments and protocols.
Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine is a field of medicine that focuses on developing therapies that can help the body regenerate and repair damaged or diseased tissues and organs. This is achieved by using various types of cells, including stem cells, to help stimulate the body's natural healing processes.
Regenerative medicine uses stem cells, which have the ability to differentiate into different cell types, such as nerve cells, muscle cells, and blood cells, among others. These cells can be sourced from various places in the body, such as bone marrow, adipose tissue, or the umbilical of a live birth.
The goal of regenerative medicine is to develop therapies that can treat a wide range of conditions, including injuries, genetic disorders, and degenerative diseases, such as osteoarthritis, Alzheimer's disease, and heart disease, among others.
The potential of regenerative medicine is still being explored, but it offers promising opportunities to develop new treatments and improve patient outcomes.
Mesenchymal stem cells, derived from the umbilical cord of a live birth (U-MSC), serve as a potent repair system in the body.
These cells have the ability to divide and create an optimal environment for tissue repair, modulate immune responses, and reduce inflammation. U-MSC stem cells effectively target areas of degeneration, building, repairing, and growing new tissue.
Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells are currently the most potent biologic available in the field of regenerative medicine.
Umbilical cord-derived stem-cell exosomes (U-MSC Exosomes) are tiny vesicles released by U-MSCs and are approximately 1000 times smaller than the mesenchymal stem cells from which they originate. These exosomes are packed with bioactive molecules that act as messengers between cells.
These lipid-lined nano vesicles carry potent anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and regenerative signals to damaged tissues and organs, facilitating intercellular communication throughout the body.
This capability places U-MSC exosomes at the forefront of regenerative medicine, making them a crucial component in enhancing clinical outcomes for many medical conditions.
Stem cells are living cells with the capacity to self-renew and differentiate into various cell types. This ability allows them to repair and regenerate damaged tissues, making them powerful tools in regenerative medicine. Stem cells have a nucleus, enabling them to replicate and participate in long-term tissue regeneration by transforming into different cell types.
Exosomes, on the other hand, are not cells but extracellular vesicles produced and secreted by stem cells, among others. They are significantly smaller than stem cells (roughly 100 times smaller) and lack a nucleus. Exosomes act as messengers, delivering bioactive molecules such as proteins, RNA, and growth factors to other cells. Though they cannot replicate, exosomes are critical for enhancing communication between cells, modulating inflammation, and promoting tissue healing.
In essence, while stem cells provide a direct source of new cells for regeneration, exosomes facilitate healing by enhancing cellular communication and guiding repair processes.
At Omni-Stem, we specialize in the use of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (U-MSCs), a type of perinatal stem cell. These cells are harvested from the umbilical cord tissue, which is a rich source of regenerative cells. U-MSCs share the broad differentiation potential and low immunogenicity characteristic of perinatal stem cells, making them less likely to provoke an immune response in recipients.
The advantages of using U-MSCs include their ease of collection and the non-invasive nature of their sourcing, which involves no harm to the mother or newborn. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells are increasingly being recognized and utilized for their significant therapeutic potential in regenerative medicine, without the ethical concerns associated with embryonic stem cells.
At Omni-Stem we source our umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and U-MSC derived exosomes through a collaborative partnership with the National University in Medellín, Colombia. We work closely with a skilled team of biotechnologists and a fertility clinic, which provides us with donated umbilical cords. The harvesting and preservation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (U-MSCs) is a delicate and highly technical procedure carried out in three phases to ensure the viability and effectiveness of the cells for therapeutic applications:
Donor Suitability
This stage involves a comprehensive evaluation of umbilical cord donors, which includes DNA and laboratory analyses to ensure the integrity and viability of the U-MSC stem cells obtained.
Harvesting and Preservation
This phase emphasizes the collection and preservation of the umbilical cord, typically discarded postpartum and the extraction and laboratory expansion of multipotent cells and their derived exosomes.
Expansion and Testing
The stem cells used for therapeutic applications are verified by a third party lab and expanded in our laboratory, in this phase we process the extraction of the U-MSC derived exosomes.
Our team in Colombia produces some of the highest-quality biologics available globally. While similar work is conducted in countries like South Korea, China, and Russia, our focus is distinct in emphasizing both exosome and mesenchymal U-MSC therapies.
The preparation required before U-MSC (mesenchymal stem cell) therapy can vary depending on the specific treatment protocol and your medical condition. However, there are some general guidelines typically followed to ensure the best possible outcome of the therapy, including medical review, hydration, and lifestyle modifications. It is crucial to follow the specific instructions provided by our medical team regarding any preparations necessary for U-MSC stem cell therapy.
U-MSC Mesenchymal stem cells have received FDA approval, making these therapies accessible in the U.S. However, the FDA does not permit the expansion of allogenic stem cells.
Consequently, patients undergoing these therapies in the U.S. typically receive only a limited number of cells, missing out on the potential benefits of U-MSC derived exosomes.
We employ a safe and controlled process in our laboratory to expand these cells, allowing us to administer tens of millions of U-MSCs as well U-MSC Exosomes to patients, which significantly enhances treatment outcomes.
This is a key reason many individuals travel to Colombia to seek advance Regenerative Medicine treatments at OmniStem.
Treatments Procedures
Most of our protocols typically take about 1 hour with minimal downtime. However, considering that a patient care plan may involve multiple procedures, the entire process, including onboarding, treatment, and medical supervision, can take up to 4 days.`
The age restrictions for U-MSC (umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell) therapy can vary depending on the specific treatment protocol and the patient's medical condition. Generally, there is no maximum age limit for MSC therapy as long as the patient is healthy enough and deemed a suitable candidate.
Like any medical treatment, MSC (mesenchymal stem cell) therapy may have some risks and potential complications. The specific risks and side effects of MSC therapy can vary depending on the patient's medical condition, the specific treatment protocol, and individual response to the therapy. It is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of MSC therapy with a qualified healthcare professional before undergoing the treatment. Your healthcare professional will help you weigh the potential risks against the benefits and determine if MSC therapy is appropriate for your medical condition. They will also monitor you closely during and after the treatment to minimize the risk of complications and to ensure the best possible outcome.
U-MSC stem cell treatments are considered specialized and are generally not covered by insurance plans.
The duration of the effects of MSC (mesenchymal stem cell) therapy can vary depending on various factors, including the specific medical condition being treated, the type of stem cell therapy used, and the individual patient's response to the treatment. In some cases, patients may experience long-lasting or permanent improvements in their symptoms after undergoing MSC therapy. For example, in some patients with osteoarthritis, MSC therapy has improved joint pain and function that can last for several years.
However, in other cases, the effects of MSC therapy may be more temporary, and patients may require repeat treatments to maintain their benefits. For example, in patients with autoimmune conditions such as multiple sclerosis, MSC therapy may provide temporary relief from symptoms, but the effects may gradually diminish over time.
The specific eligibility criteria for regenerative MSC (mesenchymal stem cell) therapy can vary depending on the patient's medical condition, the specific treatment protocol, and the stem cell provider's guidelines. However, here are some general factors that may make you a good candidate for MSC therapy:
You have a medical condition that may benefit from regenerative therapy: MSC therapy may be appropriate for various medical conditions, including orthopedic injuries, neurological disorders, autoimmune diseases, and more. Your healthcare professional can help determine if your medical condition is appropriate for MSC therapy.
You have tried other treatments without success: U-MSC therapy may be appropriate if you have tried others without success or if those treatments have not provided sufficient relief from your symptoms.
You are in good overall health: U-MSC therapy may not be appropriate for patients with certain underlying health conditions or risk factors, such as a weakened immune system, a history of cancer, or a history of blood clotting disorders. Your healthcare professional will evaluate your overall health to determine if you are a suitable candidate for MSC therapy.
You are willing to commit to the treatment process: MSC therapy typically involves multiple injections or infusions over weeks or months. It is important to be willing and able to commit to the treatment process to achieve the best possible outcomes.
It is important to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine if MSC therapy is appropriate for your specific medical condition and to discuss any eligibility criteria or concerns you may have. Your healthcare professional can help guide you through the treatment process and provide personalized recommendations based on your needs and medical history.
The combination of regenerative stem cell therapy with other treatments or medications will depend on your specific medical condition and the advice of your healthcare professional. In some cases, it may be safe and appropriate to combine MSC (mesenchymal stem cell) therapy with other treatments or medications to achieve the best possible outcome.
For example, MSC therapy may be combined with physical therapy or anti-inflammatory medications to help manage pain and improve function in orthopedic injuries. In neurological disorders, MSC therapy may be combined with medications or other therapies to help improve cognitive function or reduce symptoms. However, it is important to inform your healthcare professional of all medications, supplements, or other treatments you are currently using before undergoing MSC therapy. Some medications or treatments may interact with the stem cells or interfere with the therapeutic effects of MSC therapy.
Additionally, it is important to follow your healthcare professional's advice and guidance regarding any adjustments to your current treatment plan or medications. Your healthcare professional can help determine if MSC therapy is appropriate in combination with other treatments or medications and provide personalized recommendations based on your individual needs and medical history.
The timeline for seeing results from U-MSC (mesenchymal stem cell) therapy can vary depending on the specific medical condition, the type of stem cell therapy used, and the individual patient's response to the treatment. In some cases, patients may notice improvements in their symptoms within a few weeks of starting MSC therapy, while in other cases, it may take several months or longer to see results. It is important to remember that MSC therapy is not a magic bullet and may not work for everyone. MSC therapy aims to help promote healing and regeneration within the body, but the extent and duration of the therapeutic effects can vary from patient to patient.
Your healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance on what to expect from U-MSC therapy based on your medical condition and treatment plan. They can also monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan as needed to help optimize your outcomes.
Overall, OmniStem is committed to providing its patients and the broader community with educational resources that can help them make informed decisions about their healthcare and understand the potential benefits of U-MSC therapy.
General Treatment Information
To schedule a consultation with an OmniStem healthcare professional, please begin by filling out our Prescreening Questionnaire.
This initial step helps us assess your eligibility and develop a treatment plan tailored specifically for you.
After our medical team approves the viability of the treatment for your case, you can schedule a non-obligatory video consultation. During this session, our medical team will discuss your medical history, health condition and treatments goals.
You are welcome to bring a companion to your stem cell wellness retreat at Omni-Stem in Colombia. Having a supportive friend or family member with you during your treatment and recovery can be highly beneficial. Additionally, we offer all-inclusive accommodations for you and your companion to enjoy a wellness retreat in Colombia that you'll never forget.
Yes, there are some specific preparations that you need to do before coming to our clinic for MSC Stem Cell treatment. These preparations may include:
Reviewing and filling out all necessary medical forms and documents. Providing detailed medical history, current medications, and any other relevant health information to our medical team. Avoid non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen, for several days before treatment unless prescribed by a physician. Stopping all blood-thinning medications or supplements, such as warfarin, heparin, or fish oil supplements, at least a week before the treatment. Stopping any immunosuppressive medications, such as corticosteroids or methotrexate, at least a week before treatment unless advised otherwise by your physician. Drinking plenty of water in the days leading up to your appointment to ensure proper hydration.
Our medical team will provide more detailed instructions and recommendations based on your health status and medical history during your consultation.
Our staff at OmniStem speaks English and Spanish. We understand the importance of clear communication between our patients and the medical team, and we strive to ensure that all patients feel comfortable and well-informed throughout the treatment process.
Certainly, we understand the importance of hearing from former patients about their experience with MSC stem cell treatment. However, we prioritize the privacy of our patients and do not disclose their personal information. Nevertheless, we have a wealth of patient testimonials and success stories that we share on our website and social media platforms. We take pride in our high patient satisfaction rate and encourage you to reach out to our team to learn more.
At Omni-Stem we have treated a variety of conditions with MSC stem cell therapy, including but not limited to: Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis, Parkinson's disease, Multiple sclerosis, Diabetes, COPD, Autoimmune diseases, Spinal cord injuries, Stroke, Traumatic brain injuries, and Autism.
It's important to note that while U-MSC stem cell therapy has shown promising results in treating these conditions, it may not be suitable for everyone. It's essential to consult with a medical professional to determine if U-MSC stem cell therapy is viable for your specific condition.
Post treatment and Follow-up
There are some specific instructions that you should follow during the recovery period after receiving an MSC (mesenchymal stem cell) umbilical cord cell infusion. These instructions may vary depending on your individual medical condition, the type of MSC therapy you received, and other factors, so it is important to follow the guidance provided by your healthcare professional at OmniStem.
Some general guidelines that may apply to many patients include:
Rest and Recovery: It is important to rest and avoid strenuous activities for several days after receiving U-MSC therapy. This will give your body time to recover and may help optimize the effectiveness of the treatment.
Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids can help support your body's natural healing processes and may help reduce the risk of complications after MSC therapy.
Medication: Your healthcare professional may prescribe medications to help manage pain, inflammation, or other symptoms after MSC therapy. Be sure to follow the instructions provided and let your healthcare professional know if you experience any side effects.
Follow-up: It is important to attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your healthcare professional to monitor your progress and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
The frequency of follow-up appointments after MSC (mesenchymal stem cell) therapy can vary depending on various factors, including the type of treatment received, the specific medical condition being treated, and the individual patient's response to the treatment. Typically, patients receiving U-MSC therapy at OmniStem our clinic in Colombia will have a follow-up appointment before leaving the clinic.
During this appointment, your healthcare professional will guide you on what to expect during the recovery period and may recommend a specific follow-up schedule based on your needs. Sometimes, patients may be advised to return to the clinic for follow-up appointments in the months following treatment. These appointments may include imaging or other diagnostic tests to monitor the progress of the treatment, as well as consultations with healthcare professionals to assess the effectiveness of the therapy and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
The need for medication or a special diet after MSC (mesenchymal stem cell) stem cell treatment can vary depending on the individual patient's medical condition, the type of treatment received, and other factors. Generally, your healthcare professional at OmniStem will provide specific instructions on any medications or dietary guidelines you should follow after treatment. You may be prescribed medicines to help manage pain, inflammation, or other symptoms. Follow the instructions provided by your healthcare professional and let them know if you experience any side effects or have concerns about your medication regimen.
Sometimes, your healthcare professional may recommend a specific diet or dietary supplements to support your recovery after MSC therapy. This may include foods or supplements high in protein, vitamins, or other nutrients to help keep your body's natural healing processes.
Lifestyle Modifications: Depending on your medical condition, your healthcare professional may recommend specific lifestyle modifications to help support your recovery after MSC therapy. This may include changes to your exercise routine, recommendations to avoid certain activities or substances that could interfere with the healing process or other guidelines to help promote overall health and wellness.
Following any instructions provided by your healthcare professional at OmniStem is important to help ensure a safe and effective recovery after MSC therapy. If you have any questions or concerns about medication, diet, or lifestyle modifications after your treatment, be sure to discuss these with your healthcare professional.
The type and amount of physical activity allowed during the recovery period after MSC stem cell treatment can vary depending on the individual patient's medical condition, the type of treatment received, and other factors.
Following any specific guidelines provided by your healthcare professional at DVC Stem is essential to help ensure a safe and effective recovery. Sometimes, your healthcare professional may recommend specific types of physical activity or exercise that can help support your recovery after U-MSC therapy.
This may include low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling that can help improve circulation and promote healing without putting excessive stress on the body. However, it is crucial to avoid any strenuous or high-impact activities that could interfere with the healing process or cause further injury. Your healthcare professional may provide specific guidelines on what activities are safe and appropriate during recovery. It is also important to listen to your body during recovery and avoid pushing yourself too hard too soon. Rest and adequate recovery time are essential for allowing your body to heal and maximizing the benefits of MSC therapy.
If you experience any complications or side effects after your MSC (mesenchymal stem cell) stem cell treatment, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. Although MSC therapy is generally safe, like any medical procedure, there is always a risk of side effects or complications.
Some potential side effects of MSC therapy can include pain, swelling, or bruising at the site of the infusion, as well as fever, chills, or other symptoms of infection. Sometimes, patients may also experience allergic reactions to stem cells or other treatment components. If you experience any of these symptoms or other complications after your MSC therapy, it is important to contact your healthcare professional at OmniStem as soon as possible. They can provide you with guidance on how to manage your symptoms and may recommend additional testing or treatment as needed.
The effects of MSC therapy can last for varying lengths of time, depending on the individual patient and their specific medical condition. Some patients may experience long-term improvements in their symptoms, while others may require additional treatments to maintain the effects of the stem cells.
To maximize the potential benefits of MSC therapy, following specific guidelines provided by your healthcare professional at OmniStem is essential. It may include following a particular diet or exercise regimen, taking medications as prescribed, and attending follow-up appointments as recommended. By taking an active role in your recovery and following the guidance of your healthcare professional, you can help ensure the best possible outcomes from your MSC stem cell treatment.
Yes, it may be possible to receive additional MSC (mesenchymal stem cell) stem cell treatments in the future if needed. The decision to undergo further treatments will depend on various factors, including the patient's individual medical condition, the type of treatment received, and the effectiveness of any previous treatments. At OmniStem, your healthcare professional will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan based on your individual needs and goals. This may include a combination of treatments and therapies designed to help you achieve the best possible outcomes.
Travel and Accommodations
Our stem cell therapy clinic is located in the beautiful city of Pereira, Colombia. Pereira is a vibrant city located in the coffee region of Colombia and is known for its rich culture, friendly people, and stunning scenery. We have experienced medical professionals and medical facilities to provide U-MSC stem cell and derived exosomes therapy.
Colombia has become a tourist destination for wellness for thousands of people who consider this country the ideal place to perform their medical and cosmetic procedures. This is due to its world-class professionals, amazing facilities, such as clinics, airports, hotels, as well as numerous entertainment and cultural offerings for its visitors. Here are some of the reasons why to choose Colombia for stem cell treatment:
Experienced healthcare professionals: Colombia has a well-established healthcare system with experienced world-class medical professionals.
Advanced medical facilities: Many medical facilities in Colombia are equipped with state-of-the-art equipment and facilities, making them well-suited for advanced medical procedures.
Cost-effective treatment: Stem cell treatment in Colombia is often more affordable than in other countries, such as the United States or Western Europe, while still maintaining high-quality standards.
Accessibility: Colombia is easily accessible from North and South America, making it a convenient location for patients from these regions.
Tourist attractions: Colombia has a rich culture, history, and beautiful scenery, making it an attractive destination for medical tourism.
Depending on your needs Omni-Stem offers both options, comfortable hotel or private villas accommodation. All our locations have all the amenities to make your stay pleasant and relaxing in connection with yourself.